The Physics of Information: Quantum Potentiality to Classical Actuality of Your Experiential Reality9/20/2018 by Alex Vikoulov “A quantum possibility is more real than a classical possibility, but less real than a classical reality.” -Boris Tsirelson John Archibald Wheeler was one of the first prominent physicists to propose that reality might not be wholly physical, in some sense, our cosmos must be a “participatory” phenomenon requiring the act of conscious observation — and thus consciousness itself. Wheeler also drew attention to implicit connection between physics and information theory, which was invented in 1948 by mathematician Claude Shannon. Just as physics builds on elementary particles, the quanta, defined by measurement, so does information theory. Its “quantum” is the binary unit, or bit, which is a signal represented by one of two choices: yes or no, plus or minus, zero or one. Ironically, Wheeler’s 'it from bit' implies that a “theory of everything” will always be a work in progress, and that truth is something subjectively created rather than objectively apprehended. “I do take 100 percent seriously the idea that the world is a figment of the imagination,” Wheeler used to remark. Twisting your mind to see reality from the quantum gravity viewpoint is no easy task. It might be quite a stretch to see the physical world made up of space-time-mass-energy as a formless fog of potentiality. Physicists face the same hard problem as neuroscientists do: the problem of bridging objective description and subjective experience. Physics has encountered consciousness. Quantum theory says an object remains in a superposition of possibilities until observed. We can consider a quantum state as being about our knowledge rather than a direct description of physical reality. The physics of information just may be that bridging of quantum-to-digital reality of subjective experience. We are now at the historic juncture when quantum computing could reveal quantum information processing underpinnings of subjectivity. INTERPRETATIONS OF QUANTUM MECHANICS Quantum mechanics is a spectacularly successful theory of fundamental physics that allows us to make probabilistic predictions derived from its mathematical formalism, but the theory doesn’t tell us precisely how these probabilities should be interpreted in regards to phenomenology, i.e. our experiential reality. There are basically three main interpretive camps within quantum mechanics from which stem at least a dozen further interpretations. The first “basic” camp is ‘Many Worlds’ (Hugh Everett, 1957), ‘Many-Minds Interpretation’ (H. Dieter Zeh, 1970), which state that the different possible configurations of a system are literally parallel universes. The second camp is the ‘Pilot Wave’ mechanics, also known as the de Broglie–Bohm theory (1927), which agrees with Many Worlds about the probability amplitude, but supplements it with a “true” configuration that a physical system is “factually” in, regardless of whether or not anyone measures it. Finally, the third interpretative camp, the most popular among physicists to date, is Niels Bohr and Werner Heisenberg’s original ‘Copenhagen Interpretation’ (1927), which asserts that reality doesn’t even exist prior to your observation. The wide variety of “offshoot” interpretations within the Copenhagen camp includes but is not limited to: ‘Ensemble Interpretation’ (Max Born, 1926), ‘Quantum Logic’ (Garrett Birkhoff, 1936), ‘Time-Symmetric Theories’ (Satosi Watanabe, 1955), ‘Consciousness Causes Collapse’ (Eugene Wigner, 1961), ‘Stochastic Interpretation’ (Edward Nelson, 1966), ‘Consistent Histories’ (Robert B. Griffiths, 1984), ‘Transactional Interpretation’ (John G. Cramer, 1986), ‘Objective Collapse Theories’ (Ghirardi–Rimini–Weber, 1986, Penrose interpretation, 1989), ‘Relational Interpretation' (Carlo Rovelli, 1994), 'Cybernetic Interpretation' (Ross Rhodes, 1999), 'Information Interpretation' (Brukner-Zeilinger, 1999), 'QBism' (Christopher Fuchs, Rüdiger Schack, 2010). Let’s juxtapose the most favored interpretive models. Despite some radical differences, they have a common feature is that the wave function is regarded not as something physically real, but as a mathematical tool that encodes all that can be known about a quantum system. In his seminal 1957 ‘Many Worlds’ paper, Hugh Everett described the pluralistic nature of objective physical reality and denied the actuality of wave function collapse. However, the information content (and ontology) of this kind of reality may turn out to be zero. This is a view expressed by the British philosopher David Pearce that he refers to as ‘Zero Ontology’. Consider the classical Library of Babel. If you may recall, the Borges’ Library of Babel contains all possible books with all possible words and letters in all possible combinations. The Library of Babel has, in fact, zero information content. Yet somewhere amid the nonsense lies Encyclopedia Britannica and the complete works of Shakespeare. Withdrawing a book from the Library of Babel yields a single definite classical outcome — thereby creating information. Withdrawing more books creates more information. When we sum two ordinary non-zero probabilities, we always get a larger probability. Analogies aside, we obviously don't belong to the classical Library of Babel. Now imagine the quantum Library of Babel. Similarly, if we sum two ordinary non-zero probabilities, then we always get a bigger probability. Yet because amplitudes in QM are ‘complex numbers’, summing two amplitudes can yield zero. Scaling up to the whole of quantum multiverse and factoring in the totality of all possible worlds would yield exactly zero. As Jan-Markus Schwindt notes in his 2012 paper "Nothing Happens in the Universe of the Everett Interpretation", the Many Worlds Interpretation is therefore rather a “No World Interpretation”: no faces to be seen, no music to be heard, no aromatic roses, no black caviar, no pleasurable sex, no thoughts, no sensations. ‘Many-Minds' Interpretation and the more recent ‘Many Interacting Worlds’ hypothesis by Michael Hall (MIW, 2010) extend the original Everettian MWI by proposing that a plethora of universes have always existed side by side, and that they tenuously influence the ones near them to differentiate from themselves either at the level of individual observers as in Many Minds or by a subtle force of repulsion as in Many Interacting Worlds. Unsurprisingly, numerous objections, such as the Zero Ontology argument, that apply to the original Many-Worlds Interpretation also apply to the Many-Minds Interpretation and Many Interacting Worlds, though. Let’s revisit the quantum Library of Babel. Conjecturing solely from the Digital Philosophy perspective, at the level of Omega hypercomputer running the Omniverse with humongous but still finite storage and computational resources, “nonsensical” timelines are likely to be purged. Furthermore, human subjectivity can be actualized only when collapsing available possibilities into a single probabilistic outcome experienced as a conscious moment (~10/sec). From the computationalist perspective, the Many Worlds Interpretation is simply incomplete: no collapse -- no conscious experience.* Video: A Critique of the Many Worlds Interpretations - Inspiring Philosophy  *This article is abridged from "The Syntellect Hypothesis: Five Paradigms of the Mind's Evolution" by Alex M. Vikoulov, available now on amazon.com, bn.com, audible.com and directly from EcstadelicNET webstore. *The full story is also available at Premium Access section of this website - Sign up for Premium Access The Pilot Wave theory, also known as 'Bohmian Mechanics', has its army of proponents seeking objective uniformity tantalizingly streamlined into a singular deterministic universal worldline with "cosmic time" ticking out there in the Universe at large and accompanied by the universal pool of subatomic “billiard balls”. This clearly outdated picture of the world is “not even wrong” — you can't possibly import Newtonian classicality into the quantum realm — that would collapse the entire mathematical structure of the M-theoretic Universe/Multiverse/Omniverse as we know it. If given a choice between M-theory and the Pilot Wave theory, most respectable scientists would probably choose the former. It would also be like trying to compute the Universe on a classical digital computer which is not only a step backwards in our understanding of the world but a logical impossibility. Many Worlds and Pilot Wave interpretations are completely deterministic which cannot be right in the world based on probabilities at all levels. As we've discussed elsewhere, 'syntactic freedom' of expression is what defines us as freewilling conscious entities amidst our inherently probabilistic reality. This is perhaps the main reason why the Copenhagen interpretative camp has been on the right track since the discovery of quantum mechanics in the roaring 20's of the past century. Bear with me, I have good news and bad news for the Many Worlds interpretative camp. The good news is that indeed one can assume the God's eye perspective on our reality where all conceivable and inconceivable timelines and events happen. In this view, perhaps, our entire Universe can be "perceived" as an elementary particle of sorts in a universe up. The bad news for MWI supporters is that this God's eye view has nothing to do with your conscious experience. Just like absent-minded people may get stuck in revolving doors, MWI-ers get stuck "forever" in the tourniquet never to exit. As for the Bohmian Mechanics camp, I'm afraid I only have the bad news. Not only the Universe is presumed to be reduced to a mechanical system but free will and consciousness are consequently reduced to a by-product of mechanistic interactions. If our world can't be possibly computed on a classical digital computer, how can this be done when the Bohmians reduce it to an "abacus"? We all are internal dynamic energy of the Universe — and it's not even a metaphor — there would be no dynamics whatsoever in the absence of us subjective participants. This “participatory realism” I call ‘Experiential Realism’ is best captured by interpretations nested in the Copenhagen Interpretation camp while Many Worlds, Objective Collapse and Pilot Wave attempt to “objectify” it. Years ago Many Worlds interpretation was making more sense to me up until I gradually drifted to the Copenhagen camp. At the moment, I find more appealing the Cybernetic Interpretation by Ross Rhodes, introduced in 1999 (coincidentally same year the movie The Matrix came out), followed by QBism, agent-centric interpretation proposed by Christopher Fuchs in 2010, and backed up by the Relational Interpretation by Carlo Rovelli, 1994. A rigorous model known as Relational Quantum Mechanics (RQM), developed by the prominent Italian theoretical physicist Carlo Rovelli, posits that there are no absolute — that is, observer-independent — physical properties. Instead, all physical quantities — the entire physical world — are relative to the observer, in a way analogous to motion. This is motivated by the fact that, according to quantum theory, different observers can account differently for the same sequence of events. Consequently, each observer is inferred to “inhabit” its own physical (read: virtual) world, as defined by the context of its own observations. Moreover, since both thoughts and perceptions are mental in essence, this line of reasoning points to mind as the primary substrate of Nature, the discernible states of which constitute information. The latest interpretative model, Quantum Bayesianism, or QBism, is the combination of quantum mechanics and subjective Bayesianism which views probability as a way to quantify agent-specific degrees of knowledge and future anticipation. This fusion is inspirited both by philosophical arguments for Bayesianism and its potential for dissolving some of the notorious quantum mechanical paradoxes. Introduced by physicists Christopher Fuchs and Rüdiger Schack in 2010, QBism has a lot in common with the widely adopted Copenhagen Interpretation of quantum mechanics but in QBism all probabilities are expressed as an agent’s personal degrees of belief. This is one of the points where QBism makes a crucial departure from the Copenhagen Interpretation. Since the wave function encodes probabilities, the conclusion is that the wave function itself must be agent-specific, i.e. subjective! Information-based interpretations of quantum mechanics, Digital Physics, the Holographic Principle, and the Simulation Hypothesis have endured and indeed grown immensely in popularity over the past few decades, making them major contenders in the scientific arena. Why simulation and computation make for such handily functional equivalence is that they offer a sought-after framework for solving the paradoxes of quantum mechanics. Our “transactional” world acts something like a probabilistic processing, procedurally generated computer simulation, or a virtual reality. This cybernetic model, or the 'Noocentric Model', would account for the time-tested problems of non-locality, superposition, particle-wave duality, quantum tunneling, retrocausality, and all other weirdness in quantum studies that Einstein pronounced were far too “spooky” for him to swallow. Nonetheless, quantum mechanics remains the most mathematically precise framework of how natural phenomena behave. Reality is information, and so are we. A simulation is part of the reality that simulates it — and everything we further simulate is reality from the perspective of those being simulated. Reality is, therefore, what we experience: From a physical point of view, there could be no “objective” observer fully separated from the physical system she tries to observe. In actuality, there is no objectivity — only a subjective perspective on things, i.e. individuated consciousness. Ultimately, any experiential reality is an observer-centric virtuality. The weirdness of quantum reality that remains amorphous or indefinite until measured is famously displayed by the thought experiment where Schrödinger’s cat is in a terrifying limbo, neither alive nor dead, until someone opens the box to look inside. But not to worry for the cat — subjectively, the cat (or a physicist taking its place) is always alive thanks to another thought experiment known as the 'Quantum Suicide'. Look them up if you're not familiar with any of them. I’ve also written the essay: “Quantum Immortality: Does Quantum Physics Imply You Are Immortal?” detailing both gedanken experiments. 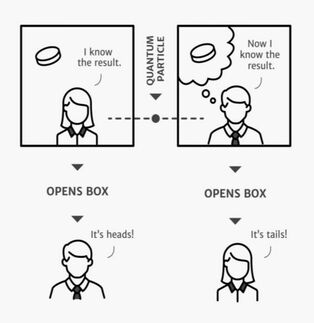 Figure 1: Renner-Frauchiger Paradox Figure 1: Renner-Frauchiger Paradox Recently published, an updated version of the Schrödinger's cat experiment sent ripples in the scientific milieu. In this Renner-Frauchiger experiment (2018) (see Figure 1), sort of like the "double Schrödinger's cat", instead of one cat we box two quantum observers — two human physicists. You can challenge me on how to interpret this thought experiment but my conclusion is that it has clearly demonstrated that a subjective (not objective, or 'no collapse' as MWI-ers would claim) wave function collapse is what determines the outcome of any observation. The subjective collapse QM interpretations such as Cybernetic Interpretation and QBism seem to get additional support of late.*  *This article is abridged from "The Syntellect Hypothesis: Five Paradigms of the Mind's Evolution" by Alex M. Vikoulov, available now on amazon.com, bn.com, audible.com and directly from EcstadelicNET webstore. *The full story is also available at Premium Access section of this website - Sign up for Premium Access Quite unlike any other branch of science, quantum physics unsurprisingly has acquired its own metaphysics, a shadow discipline, in Heisenberg’s term an “ideological superstructure”. Designed as meta-analysis of QM interpretations, this field is called ‘Quantum Foundations’, which is unintentionally ironic, because where you would expect foundations you instead find quicksand.* RELATED:  *This article is abridged from "The Syntellect Hypothesis: Five Paradigms of the Mind's Evolution" by Alex M. Vikoulov, available now on amazon.com, bn.com, audible.com and directly from EcstadelicNET webstore. *The full story is also available at Premium Access section of this website - Sign up for Premium Access Max Planck, when referring to consciousness as being the fundamental feature of reality, wrote: “Everything we call real is made of things that cannot be regarded as real." Echoing his words, Werner Heisenberg divulged that: “[T]he atoms or the elementary particles themselves are not as real; they form a world of potentialities or possibilities rather than one of things or facts.” Heisenberg interpreted the mathematics behind quantum theory to mean that reality doesn’t exist until observed. “The idea of an objective real world whose smallest parts exist objectively in the same sense as stones or trees exist, independently of whether or not we observe them... is impossible.” This seemed utterly disturbing to philosophers as well as physicists and it led Albert Einstein to say in 1952: “The theory reminds me a little of the system of delusions of an exceedingly intelligent paranoiac.” A bold, unorthodox paper by Ross Rhodes, first published in 1999 with a revised version in 2001, “A Cybernetic Interpretation of Quantum Mechanics” pre-dates Bostrom's "Are You Living in the Computer Simulation?" (2003) and Whitworth's “The Physical World as a Virtual Reality” (2008). Rhodes presents to us a well-grounded argument that the “fuzzy” physics of the quantum world can be interpreted as evidence that we are integral, dynamic part of some sort of computer-simulated reality. Rhodes argues that quantum physics resembles the deep "code layer" underlying our physical reality. For instance, quantum non-locality makes a lot of sense if you assume that all information processing for the universal hypercomputer is being done by its central GPU. In my essay “Is God the Ultimate Computer?” Part III we recount 10 broad categories of the physical world's properties, its natural phenomena and processes, and corresponding 40 M-observables to confirm the viability of the Cybernetic Interpretation of quantum mechanics.* RELATED:  *This article is abridged from "The Syntellect Hypothesis: Five Paradigms of the Mind's Evolution" by Alex M. Vikoulov, available now on amazon.com, bn.com, audible.com and directly from EcstadelicNET webstore. *The full story is also available at Premium Access section of this website - Sign up for Premium Access THE SCHRÖDINGER EQUATION: THE ONTOLOGY OF WAVE FUNCTION Quantum physics throws all the rules of classical physics out the window. In the quantum world, particles can pass through solid walls, be in two places at once, instantly communicate over infinitely large distances, and affect their past counterparts just as easily as they affect the future ones. The rules we have discovered for the behavior of quantum systems — the Schrödinger equation and so on — don’t obviously resemble the classical rules we use to describe everyday objects, notably Newton’s Laws of motion among other things in high-school physics curriculum. We spend the vast majority of our lives interacting with things that obey classical physics, i.e. Newton’s Laws, and that defines our intuition for how things “ought” to behave. When quantum physics departs from that, all of it seems incredibly weird. The Schrödinger equation, considered a cornerstone of quantum theory, in its most general time-dependent form describes the evolution of a quantum system and predicts that if certain properties of a quantum system are measured, the “classical” outcome will be quantized, meaning that only specific discrete values would appear. The equation was named after Erwin Schrödinger, who derived the equation in 1925, and was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933. All above mentioned QM interpretations are aimed to decipher this mathematical equation as to how it actually means when describing reality presented to us by our measurements. In my book “The Syntellect Hypothesis" I show that time is emergent so must be spacetime. What does it even mean? This means that spacetime is not smooth and continuous as Einstein hypothesized ad hoc but it turns out that spacetime is discretized and emerges from the substructure of reality: information, more specifically observer experiential data streams. If it sounds insane, we should remind ourselves that most contemporary ideas were once considered “crazy” until they were widely accepted and changed our picture of the world for good. The Holographic Principle, for instance, which isn’t science-fiction, but a bona fide idea in theoretical physics, along with other recent discoveries in physics, tell us that view of fundamental spacetime is doomed — along with the objects it contains and their appearance of physical causality — and must be replaced by something more fundamental, if we are to succeed in our quest for a quantum gravity theory.* RELATED:  *This article is abridged from "The Syntellect Hypothesis: Five Paradigms of the Mind's Evolution" by Alex M. Vikoulov, available now on amazon.com, bn.com, audible.com and directly from EcstadelicNET webstore. *The full story is also available at Premium Access section of this website - Sign up for Premium Access THE MEASUREMENT PROBLEM: THE OBSERVER EFFECT vs. QUANTUM EFFECTS The famed ‘Observer Effect’ which has been demonstrated in the ‘Double-Slit Experiment’ and its numerous variations, challenged one of science’s most basic tenets: that there is an objective, observable reality that exists whether we’re looking at it or not. The revelation that the act of observation, or measuring quantum effects, directly affects particles’ behavior is perplexing, to say the least, but it also suggests that a conscious observer itself is part of quantum theory. Notoriously counterintuitive quantum effects include wave-particle duality, quantum entanglement, quantum tunneling, retrocausality, and overall non-linearity of quantum systems, just to name the few usual suspects. Classical and quantum physics are well-defined in their respective realms, but grander questions have troubled physicists for decades: What links these two opposing views of reality? Why do the fundamental laws of classical physics fail at the quantum level, and can they ever be reconciled? The von Neumann–Wigner interpretation, proposed in 1961, the first of its kind to be described as "consciousness causes collapse [of the wave function]", is an interpretive model of quantum mechanics in which consciousness is postulated to be necessary for the completion of the process of quantum measurement. If the act of observation is directly tied with consciousness and results in the subjective collapse of the wave function, how are the probabilities converted into an actual, sharply defined classical outcome? As we've discussed elsewhere many reasons why decoherence cannot account for the transition from quantumness to classicality of subjective experience we can reiterate the main argument here. Just like Bohmian mechanics attempting to import the classicality of “billiard balls” into inherently probabilistic quantum realm, one can immediately comprehend the absurdity of invoking quantum decoherence as a failing physicalist assumption. In other words, it neither causes the [objective as intended] wave function collapse nor solves the measurement problem. First introduced in 1970 by the German physicist H. Dieter Zeh with Many-Minds interpretation, the concept of decoherence is actually useful for functional quantum computers when researchers try to isolate the quantum processing unit in order to prevent quantum leakage. Decoherence refers to a loss of ‘quantum coherence’ which is a fancy term for an “unentangled” quantum state. Entanglement is understood as an inevitable result of any interaction between two quantum objects. Once entangled, two objects become linked forever — they cannot abruptly “disentangle” — this quantum effect should also be true for the network of particles, in fact, all particles in the Universe since the Big Bang which is an apparent contradiction. And yet, decoherence, physicalists insist, is an essential mechanism of the quantum-classical transition. To show quantum behavior, such as interference, superposition and entanglement-induced correlations, they say, any object, no matter how big it is, depends only on how entangled it is with its environment. But, as we have established, the entire Universe is deep down non-local at the sub-quantum level, that is entangled. What are we missing here? Again, the answer is: the conscious observer. A conscious mind, a “chooser,” is still required to actualize the collapse of the wave of probabilities to crystallize it into an observer-centric classical actuality. Now, if we instead combine the top-down quantum information processing (computationalist) approach, as in the essay on Cosmo-Teleology with the ‘Conscious Instant’ (CI) hypothesis (see “The Unified Field and the Quantum Nature of Consciousness”), then we can see that each conscious instant is an integrated digital pattern of information — like a frame in the movie — whereas the mind of experimenter (conscious observer) collapses quantum mechanical potentiality into classical actuality. This is quantum information processing — from qubits of the qualia spectrum to “digits of qualia”. This led me to formulate the D-theory of Time, or ‘Digital Presentism’, for to understand our subjective experience we need to understand time.* RELATED:  *This article is abridged from "The Syntellect Hypothesis: Five Paradigms of the Mind's Evolution" by Alex M. Vikoulov, available now on amazon.com, audible.com and directly from EcstadelicNET webstore. *The full story is also available at Premium Access section of this website - Sign up for Premium Access The metaphysical principle of “unity” – that everything in the Universe is intimately interconnected – is difficult to believe in our everyday physical world where living beings and non-living objects appear separate and distinct from one another. However, since the 1930s, research in the field of quantum entanglement has suggested that at the subatomic and even deeper sub-quantum levels, everything might indeed be connected. This seemingly metaphysical weirdness of universal “oneness” has found its physics counterpart referred to as ‘non-locality’. At a fundamental level of reality, there may be no such thing as place, no such thing as distance, and no such thing as time but only information. As the quantum theory shows, our entire Universe is deep down non-local. It's one and the same with non-local consciousness. How so? Research has shown that consciousness is non-local, a scientific way of alluding to a connection within a higher dimensional order. Matter has also been shown to be non-local, which hints that matter might be an expression of consciousness. The non-locality of our physical world has been proved by John S. Bell in 1964 (by the famously known Bell's theorem) and confirmed by experimental results obtained since the early 1980s. This theoretical and experimental evidence dispelled the Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen (EPR) paradox, and with it, 'local realism'. The assumptions of materialism have been challenged ever since the discovery of quantum physics by showing that consciousness could not be ignored since observation directly affects matter...* RELATED:  *This article is abridged from "The Syntellect Hypothesis: Five Paradigms of the Mind's Evolution" by Alex M. Vikoulov, available now on amazon.com, bn.com, audible.com and directly from EcstadelicNET webstore. *The full story is also available at Premium Access section of this website - Sign up for Premium Access THE MENTAL UNIVERSE HYPOTHESIS: OBJECTIVE vs. SUBJECTIVE WAVE FUNCTION COLLAPSE Is the Universe mental or physical? Let's actually rephrase the question for ease of argumentation: Is reality mental or physical? Science often makes strides by contradicting what we take for granted, and the biggest thing everyone takes as a given is our physical world. Traditionally, scientific endeavor assumed that matter is all that exists, however, it’s not a scientific fact, it’s just a basic assumption, it should not be regarded as more than a philosophical starting point. Our senses wrap themselves around tangible objects so naturally that it’s hard to believe that our sensory apparatus may be misleading us completely. So, it becomes more than just intriguing, when any prominent theorist brings up the showcase for a different view of reality, one in which the mind creates the features of what we call “the physical world"...* RELATED:  *This article is abridged from "The Syntellect Hypothesis: Five Paradigms of the Mind's Evolution" by Alex M. Vikoulov, available now on amazon.com, bn.com, audible.com and directly from EcstadelicNET webstore. *The full story is also available at Premium Access section of this website - Sign up for Premium Access As we've seen, a number of latest QM interpretations such as RQM, Cyberneticism and Qbism support the Mental Universe hypothesis. There's nothing supernatural or mystical about this claim: Universal mind — whose ontology is still up for debates but can be extrapolated from our existential circumstance — underlies the “worldware”, a kind of software of the universal operating system accounting for our experiences of the physical world in accordance with a set of rules we call the laws of Nature. This transdimensional consciousness encompasses but far transcends any individual mind. Quantum computational dynamics of all mass-energy in the Universe correspond to mentation of the non-local ‘Transcendent Other’, just as an individual’s brain activity correlates with personal mentation. Since we all are alternate realities, each of us being a parallel "unique-verse", 'observer-centric virtuality' is possibly one of the best metaphors related to the ontology of our experiential reality. This notion eliminates unnecessary discrepancies and provides the missing inner essence of the perceptible world: Different configurations of matter and energy reflect different patterns or modes of thinking by the larger consciousness system rendering VR to the player. In other words, mind instantiates oneself into matter and energy...* RELATED:  *This article is abridged from "The Syntellect Hypothesis: Five Paradigms of the Mind's Evolution" by Alex M. Vikoulov, available now on amazon.com, bn.com, audible.com and directly from EcstadelicNET webstore. *The full story is also available at Premium Access section of this website - Sign up for Premium Access UNIVERSALITY OF QUANTUM LOGIC In the physics of information, known as Digital Physics, all natural phenomena and physical processes are thoroughly computable, with the laws of Nature acting as master algorithms factoring in undeniable universality of quantum logic. In an often-quoted remark computer scientist Tommaso Toffoli puts this quite eloquently: "In a sense, Nature has been continually computing the "next state" of the Universe for billions of years; all we have to do — and, actually, all we can do — is "hitch a ride" on this huge ongoing [quantum] computation". This universal computability of Nature is what allows us to use computers to model or "simulate" physical processes, thus greatly enhancing our abilities to understand and emulate Nature..." RELATED:  *This article is abridged from "The Syntellect Hypothesis: Five Paradigms of the Mind's Evolution" by Alex M. Vikoulov, available now on amazon.com, audible.com and directly from EcstadelicNET webstore. *The full story is also available at Premium Access section of this website - Sign up for Premium Access If C.elegans and its environment can be perfectly described in code and code can be controlled by behavioral controls applied to the computer version of the real thing, a living system is said to be replicated in code and its “description” is indistinguishable from what has been described. There would be no difference between a simulation of something at a certain level of description and the real thing. And if there is no difference between a perfect simulation and reality, and if there is nothing that will prevent us from creating such perfect simulations, at some point in the future however far off, we will be able to create virtual universes with sentient computational agents – self-conscious virtual beings. Once you accept the logic that simulated realities [will] exist, it becomes clear that with the number of simulated worlds, each containing billions or even trillions of conscious minds, the chances that we are ‘base reality’ drops to almost zero.* RELATED:  *This article is abridged from "The Syntellect Hypothesis: Five Paradigms of the Mind's Evolution" by Alex M. Vikoulov, available now on amazon.com, bn.com, audible.com and directly from EcstadelicNET webstore. *The full story is also available at Premium Access section of this website - Sign up for Premium Access I... So, it seems that hyperreality is ultimately a fractal system of progressively self-exceeding computations. In my book I argue that information does not simply describe our physical reality but it is the most fundamental “code layer” of reality. The ultimate reality is thus produced by a massively parallel Omega Hypercomputer that is most likely to have qubits at its controls for the realization of any physically possible world. In The Matrix movie Morpheus is trying to get across to Neo that everything he thinks is real is actually only information that the brain receives and translates into his unitary experiential reality. “Your mind makes it real,” says Morpheus in the “purgatory” scene. Another great scene I enjoyed watching is when a boy from the Oracle’s entourage engages Neo in chalk talk: “Do not try to bend the spoon, that's impossible! Instead, only try to realize the truth!” _ “What truth?”_ “There is no spoon!”_ “There is no spoon?”_”Then you'll see this is not the spoon that bends, it is only yourself!”* Video: A scene from "The Matrix" (1999), Warner Bros. EXPERIENTIAL REALITY: QUBITS-TO-DIGITS OF QUALIA A little while ago, the idea that our minds create reality would have seemed preposterous to most westerners. But today everyone in the West becomes a bit more susceptible to this bold new idealistic, computationalist thinking along with certain QM interpretations directly pointing to the fundamental laws of Nature emerging from consciousness. It might be mind-boggling for some people to consider that a coherent description of reality, with all its quantum oddities, can arise from nothing more than first-person subjective experiences. In these new information-based interpretations, consciousness doesn't just collapse the probabilistic wave function. Conscious experience IS the collapse of wave function....* Video: Consciousness: Our Subjective Experience - Ecstadelic Media (cc) How can we get a better grasp of the inner workings of our experiential reality? Read my new book "The Syntellect Hypothesis: Five Paradigms of the MInd's Evolution" available now on Amazon, from Barnes & Noble or directly from EcstadelicNET webstore, and be prepared to get "mind-blown!" -Alex Vikoulov P.S. That was an exclusive abridged excerpt from my new book "The Syntellect Hypothesis: Five Paradigms of the Mind's Evolution" available now on Amazon, Audible, from Barnes & Noble, and directly from EcstadelicNET webstore. *The unabridged story is also available at Premium Access section of this website - Sign up for Premium Access Tags: Physics of Information, Quantum Potentiality, Classical Actuality, Experiential Reality, Boris Tsirelson, John Archibald Wheeler, Claude Shannon, Quantum theory, quantum state, quantum-to-digital reality, subjective experience, Quantum mechanics, phenomenology, Many Worlds, Hugh Everett, Many-Minds Interpretation, H. Dieter Zeh, 19, Pilot Wave, de Broglie–Bohm theory, Niels Bohr, Werner Heisenberg, Copenhagen Interpretation, Ensemble Interpretation, Max Born, Quantum Logic, Garrett Birkhoff, Time-Symmetric Theories, Satosi Watanabe, Consciousness Causes Collapse, Eugene Wigner, Stochastic interpretation, Edward Nelson, Consistent Histories, Robert B. Griffiths, Transactional Interpretation, John G. Cramer, Objective Collapse Theories, Subjective Collapse, Noocentric Model, Ghirardi–Rimini–Weber, Penrose interpretation, Relational Interpretation, Carlo Rovelli, Cybernetic Interpretation, Ross Rhodes, QBism, Christopher Fuchs, Ruediger Schack, David Pearce, Zero Ontology, Library of Babel, Jan-Markus Schwindt, Michael Hall, Digital Philosophy, Omega hypercomputer, Omniverse, akashic records, Bohmian mechanics, M-theory, Experiential Realism, Quantum Bayesianism, Subjective Bayesianism, Digital Physics, Holographic Principle, Simulation Hypothesis, paradoxes of quantum mechanics, virtual reality, VR model, non-locality, superposition, particle-wave duality, quantum tunneling, retrocausality, individuated consciousness, observer-centric virtuality, Quantum Immortality, Quantum Physics, QM interpretations, Renner-Frau chiger experiment, Quantum Foundations, Max Planck, Albert Einstein, Ross Rhodes, Newton’s Laws, Schrödinger equation, Adam Becker, Isaac Newton, Double-Slit experiment, wavicles, cosmology, relativistic physics, Anthony Peake, Zero Point Field, Unified Field, Observer Effect, quantum effects, von Neumann–Wigner interpretation, quantumness, quantum leakage, decoherence, quantum coherence, quantum-classical transition, qualia space, classical actuality, D-theory of time, Digital Presentism, Big Bang, Kirno Sohochari, quantum entanglement, non-local consciousness, bi-mind, philosophical idealism, Richard Conn Henry, Mental Universe hypothesis, Erwin Schrödinger, John von Neumann, Andre Linde, Large Hadron Collider, Bernardo Kastrup, Quantum Anomalies, Mind Over Substrates, Web v.5.0, Metaverse, Gray Scott, Simulation Singularity, virtual worlds, Omega Point Cosmo-Teleology, qualia, RQM, Cyberneticism, Qbism, Universal mind, universal operating system, transdimensional consciousness, Transcendent Other, cosmic self, Theta point, temporal singularity, panpsychism, cosmopsychism, physicalism, Transcendent Self, philosophical treatise, Muriel Rukeyser, pantheistic solipsism, Digital Pantheism, Mandela Effect, Fiona Broome, Nelson Mandela, master algorithm, Tommaso Toffoli, Tom Campbell, Edward Fredkin, Hans Moravec, Stephen Wolfram, Ben Goertzel and Ray Kurzweil, quantum neural networks, quantum biology, procedurally generated games, Schrödinger's cat, VR physics engine, Simulation Argument, Nick Bostrom, Emergent Multiverse, hyperreality, Is God The Ultimate Computer? Omega Hypercomputer, The Matrix, Morpheus, Neo, Conscious experience, delayed-choice experiments, phenomenological experience, It from Qubit, reality is in consciousness, AGI *Image Credit: "The Matrix" (1999), Warner Bros. About the Author: Alex Vikoulov is a Russian-American futurist, evolutionary cyberneticist, philosopher of mind, CEO/Editor-in-Chief of Ecstadelic Media Group, painter, essayist, media commentator, author of "The Syntellect Hypothesis: Five Paradigms of the Mind's Evolution," "The Origins of Us: Evolutionary Emergence and The Omega Point Cosmology," "The Physics of Time: D-Theory of Time & Temporal Mechanics," "The Intelligence Supernova: Essays on Cybernetic Transhumanism, The Simulation Singularity & The Syntellect Emergence," "Theology of Digital Physics: Phenomenal Consciousness, The Cosmic Self & The Pantheistic Interpretation of Our Holographic Reality," "NOOGENESIS: Computational Biology," "TECHNOCULTURE: The Rise of Man." Self-described neo-transcendentalist, cosmist and transhumanist singularitarian. Lives in Burlingame, California (San Francisco Bay Area). More Bio... Author Website: www.alexvikoulov.com e-mail: [email protected]
6 Comments
Shahriar Mazandi
9/23/2018 11:34:04 am
I do apologise for not having read the entire article but am preparing legal papers (which I ought to be doing now rather than reading this very interesting piece) but many thought provoking matters are brought up.
Reply
9/24/2018 05:45:19 am
John David Best has his web site Vida İnstitute. He put my articles page in 'Timeflow Theory' 'http://vidainstitute.org/?page_id=656'. Vida Institute is intersting site. And my web site is www.timeflow.org
Reply
jack kybird
10/27/2018 03:42:30 am
What I found the most awesome and inspiring paragraphs from this article. Quantum Theory really is out of this world.
Reply
Neffey
10/1/2019 10:37:13 am
[[[and it's not even a metaphor]]]
Reply
Thank you for sharing this enlightening exploration of the intersection between physics and consciousness. Your blog post has sparked a newfound curiosity in me to delve deeper into the mysteries of our experiential reality and the role of information in shaping our perception of the world.
Reply
Leave a Reply. |
Categories
All
Recent Publications The Cybernetic Theory of Mind by Alex M. Vikoulov (2022): eBook Series The Syntellect Hypothesis: Five Paradigms of the Mind's Evolution by Alex M. Vikoulov (2020): eBook Paperback Hardcover Audiobook The Omega Singularity: Universal Mind & The Fractal Multiverse by Alex M. Vikoulov (2022): eBook THEOGENESIS: Transdimensional Propagation & Universal Expansion by Alex M. Vikoulov (2021): eBook The Cybernetic Singularity: The Syntellect Emergence by Alex M. Vikoulov (2021): eBook TECHNOCULTURE: The Rise of Man by Alex M. Vikoulov (2020) eBook NOOGENESIS: Computational Biology by Alex M. Vikoulov (2020): eBook The Ouroboros Code: Reality's Digital Alchemy Self-Simulation Bridging Science and Spirituality by Antonin Tuynman (2019) eBook Paperback The Science and Philosophy of Information by Alex M. Vikoulov (2019): eBook Series Theology of Digital Physics: Phenomenal Consciousness, The Cosmic Self & The Pantheistic Interpretation of Our Holographic Reality by Alex M. Vikoulov (2019) eBook The Intelligence Supernova: Essays on Cybernetic Transhumanism, The Simulation Singularity & The Syntellect Emergence by Alex M. Vikoulov (2019) eBook The Physics of Time: D-Theory of Time & Temporal Mechanics by Alex M. Vikoulov (2019): eBook The Origins of Us: Evolutionary Emergence and The Omega Point Cosmology by Alex M. Vikoulov (2019): eBook More Than An Algorithm: Exploring the gap between natural evolution and digitally computed artificial intelligence by Antonin Tuynman (2019): eBook Our Facebook Pages
A quote on the go"When I woke up one morning I got poetically epiphanized: To us, our dreams at night feel “oh so real” when inside them but they are what they are - dreams against the backdrop of daily reality. Our daily reality is like nightly dreams against the backdrop of the larger reality. This is something we all know deep down to be true... The question then becomes how to "lucidify" this dream of reality?"— Alex M. Vikoulov Public Forums Our Custom GPTs
Alex Vikoulov AGI (Premium*)
Be Part of Our Network! *Subscribe to Premium Access Make a Donation Syndicate Content Write a Paid Review Submit Your Article Submit Your Press Release Submit Your e-News Contact Us
|